Welcome to the resource topic for 2021/1258
Title:
Bit Security as Computational Cost for Winning Games with High Probability
Authors: Shun Watanabe, Kenji Yasunaga
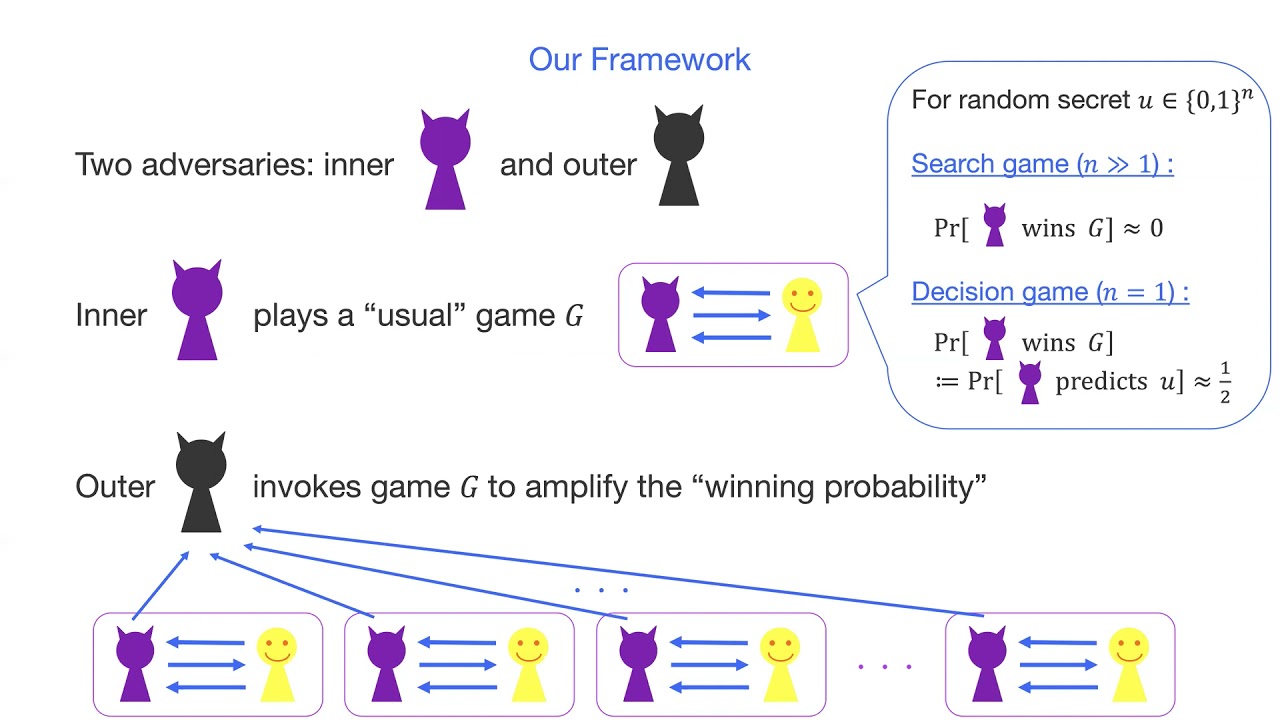
Abstract:We introduce a novel framework for quantifying the bit security of security games. Our notion is defined with an operational meaning that a \lambda-bit secure game requires a total computational cost of 2^\lambda for winning the game with high probability, e.g., 0.99. We define the bit security both for search-type and decision-type games. Since we identify that these two types of games should be structurally different, we treat them differently but define the bit security using the unified framework to guarantee the same operational interpretation. The key novelty of our notion of bit security is to employ two types of adversaries: inner adversary and outer adversary. While the inner adversary plays a usual'' security game, the outer adversary invokes the inner adversary many times to amplify the winning probability for the security game. We find from our framework that the bit security for decision games can be characterized by the information measure called the Rényi divergence of order $1/2$ of the inner adversary. The conventional advantage,‘’ defined as the probability of winning the game, characterizes our bit security for search-type games. We present several security reductions in our framework for justifying our notion of bit security. Many of our results quantitatively match the results for the bit security notion proposed by Micciancio and Walter in 2018. In this sense, our bit security strengthens the previous notion of bit security by adding an operational meaning. A difference from their work is that, in our framework, the Goldreich-Levin theorem gives an optimal reduction only for ``balanced’’ adversaries who output binary values in a balanced manner.
ePrint: https://eprint.iacr.org/2021/1258
Talk: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2OtEnDiZux8
Slides: https://iacr.org/submit/files/slides/2021/asiacrypt/asiacrypt2021/73/slides.pdf
See all topics related to this paper.
Feel free to post resources that are related to this paper below.
Example resources include: implementations, explanation materials, talks, slides, links to previous discussions on other websites.
For more information, see the rules for Resource Topics .