Welcome to the resource topic for 2018/480
Title:
On Distributional Collision Resistant Hashing
Authors: Ilan Komargodski, Eylon Yogev
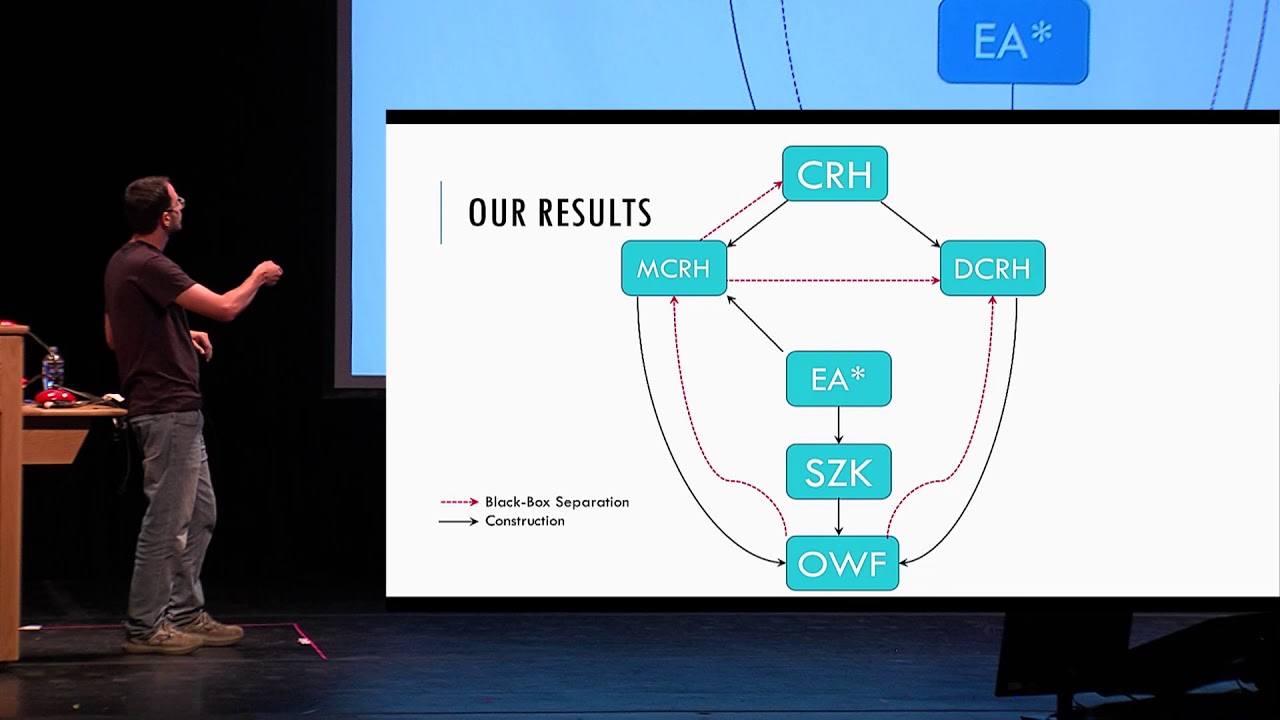
Abstract:Collision resistant hashing is a fundamental concept that is the basis for many of the important cryptographic primitives and protocols. Collision resistant hashing is a family of compressing functions such that no efficient adversary can find any collision given a random function in the family. In this work we study a relaxation of collision resistance called distributional collision resistance, introduced by Dubrov and Ishai (STOC '06). This relaxation of collision resistance only guarantees that no efficient adversary, given a random function in the family, can sample a pair (x,y) where x is uniformly random and y is uniformly random conditioned on colliding with x. Our first result shows that distributional collision resistance can be based on the existence of multi-collision resistance hash (with no additional assumptions). Multi-collision resistance is another relaxation of collision resistance which guarantees that an efficient adversary cannot find any tuple of k>2 inputs that collide relative to a random function in the family. The construction is non-explicit, non-black-box, and yields an infinitely-often secure family. This partially resolves a question of Berman et al. (EUROCRYPT '18). We further observe that in a black-box model such an implication (from multi-collision resistance to distributional collision resistance) does not exist. Our second result is a construction of a distributional collision resistant hash from the average-case hardness of SZK. Previously, this assumption was not known to imply any form of collision resistance (other than the ones implied by one-way functions).
ePrint: https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/480
Talk: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KoEc86KdiEg
Slides: https://crypto.iacr.org/2018/slides/28816.pdf
See all topics related to this paper.
Feel free to post resources that are related to this paper below.
Example resources include: implementations, explanation materials, talks, slides, links to previous discussions on other websites.
For more information, see the rules for Resource Topics .